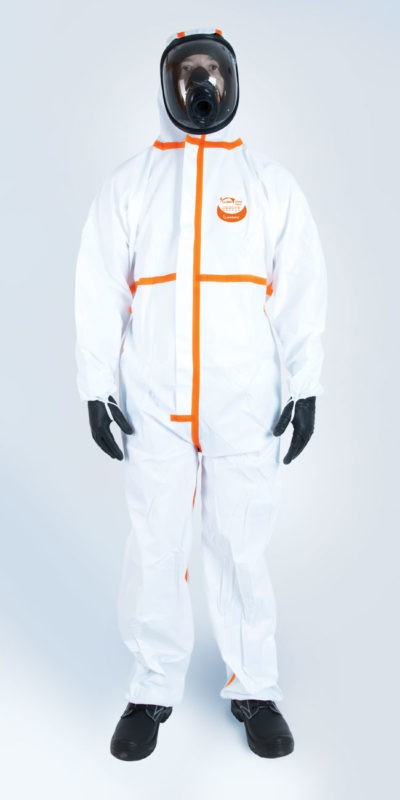

TYPE 4/5/6 WEEPRO MAX PLUS COVERALL

Request for recommendation
Find a distributor

Need information about : PROFESSION SHEET : WOOD INDUSTRIES ?

22 January 2019
This wood industry guide helps woodworkers to optimize choice of protective coveralls when machining, sanding and wood processing
PROFESSION SHEET : WOOD INDUSTRIES.pdfWood workers may come into contact with hazardous chemicals contained in wood treatment products, paint removers, binders, adhesives, varnishes or paints. WeeSafe has designed a complete range of coveralls against projections of hazardous dust, or splashing of liquid impregnation products for the wood industries.
Sawing and particularly sanding operations generate a large amount of very fine dust. Wood dust is harmful by skin contact. Their dangerousness level depends on the varieties of wood species (hardwoods, conifers, exotic woods). In addition, treated wood contains chemicals such as formaldehyde.
Preparing products: Handling of chemical and impregnation products
Applying products with a brush and a spray: Applying adhesives, paints, varnishes, paint removers, stains composed of: epoxy resins, acetone, rosin, aminoplast resin, isocyanate formaldehyde, dichloromethane.
Applying products by dipping or autoclaving: autoclaving Enclosures opening and lumber outfeeding during automated treatments.
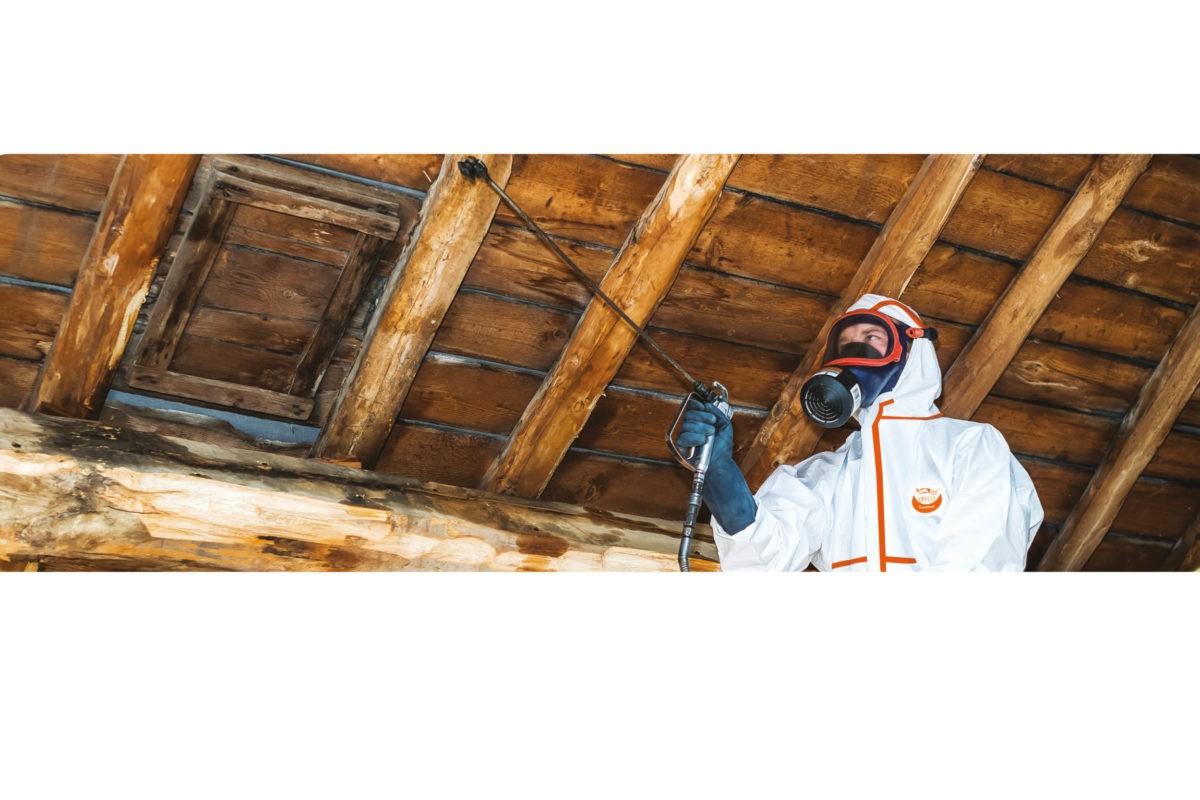
Applying a preventive or curative wood treatment with a brush: Main chemicals used: Solvents (whitespirit, xylenes), insecticides, fungicides, creosotes.
Applying a preventive or curative wood treatment with a spray: Main chemicals used : Solvents (whitespirit, xylenes), insecticides, fungicides, creosotes.
Cleaning tools: Solvent handling such as acetone
Click here to discover our profession sheet – wood industries